When most people hear about Stem Cell Treatments, they imagine the cells transforming into brand new cartilage, nerve cells, or even entire organs. The reality is more complex.
Modern research shows that while stem cells can turn into other cells in theory, this is not what usually happens in patients.
Instead, the real power of stem cell therapy comes from the signals they send, calming inflammation, protecting healthy cells and guiding the body’s own repair processes .
This article will break down exactly how stem cell treatments work, what kinds of cells clinics use and what you can realistically expect if you’re considering therapy.
We’ve collated this information after reviewing over 100 research papers and clinical trials published since 2018. To explore the latest studies by condition, visit our Research section
How does Stem Cell Therapy work in 2025?
Stem cell therapy works mainly by calming inflammation and helping the body repair itself, with studies showing that mesenchymal stem cells rarely turn into new cells.
We know there’s a lot of talk about Stem Cell “turning into new cells” but the data isn’t confirming this theory for Mesenchymal Stem Cells. These are the main types of Stem Cells used in treatments today.
Researchers have identified several key mechanisms that explain how these cells may help repair the body and improve symptoms:
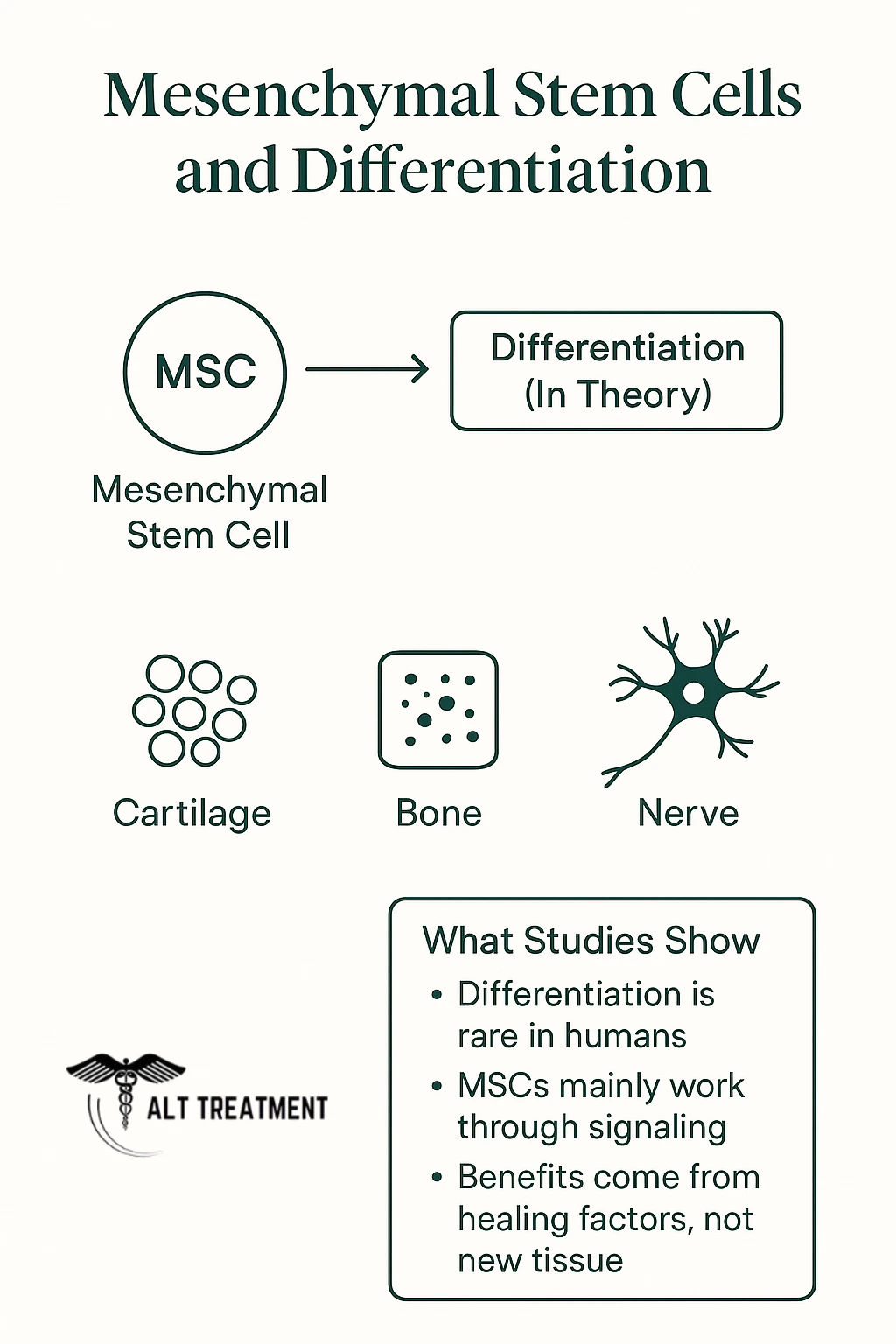
Differentiation: Turning Into New Cells
Stem cells are unique because they can transform into different cell types, such as cartilage, bone, or nerve cells. For example, in theory stem cells injected into a damaged knee may become new cartilage cells that support repair.
But in real-world human studies, when researchers use Mesenchymal Stem Cells this rarely happens. Most of the benefits seen in patients come from the signals stem cells release, not from them permanently transforming into new tissue. Scientists are still studying how to make direct differentiation more reliable, but for now, it’s not considered the main way stem cell therapy works.
Read more about differentiation and what studies show here.
Paracrine Signaling: Acting as Messengers
Today, researchers believe this is the main way stem cell therapies help patients. Instead of becoming new tissue themselves, stem cells act like messengers. They release growth factors and cytokines. Chemical signals that tell nearby cells to reduce inflammation, repair damage and protect healthy tissue.
This “cell-to-cell communication” helps create an environment where the body can begin healing itself. It’s especially important in conditions such as spinal cord injuries, autoimmune diseases, and brain disorders, where calming inflammation and supporting natural repair are more valuable than trying to replace entire cells or tissues.
Immunomodulation: Calming the Immune System
An overactive immune system can sometimes cause more damage than the original illness. Stem cells help by restoring balance, lowering harmful inflammation, and preventing the immune system from attacking healthy tissue. This is why therapies are being explored for diseases such as multiple sclerosis, Crohn’s disease and rheumatoid arthritis.
Homing: Finding the Damaged Areas
Some stem cells, particularly mesenchymal stem cells, appear to have a natural ability to “home in” on areas of injury or inflammation. Guided by chemical distress signals, they can travel through the body toward sites that need repair.
In conditions like COPD or Type 2 diabetes, this may help explain why intravenous infusions of MSCs show benefits, even though the cells don’t survive long in the body. They reach inflamed tissues, release healing signals and then fade away.
Regeneration: Rebuilding Over Time
Healing with stem cells is not immediate. Once the cells reach damaged tissue, they begin a gradual process of repair: reducing scar tissue, improving blood flow and encouraging new growth. Improvements may take weeks or months, depending on the condition and the individual, but over time this regenerative effect can lead to stronger, healthier tissue.
What Stem Cells Do Clinics Use in Treatment?
Stem Cell Clinics mainly use Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSC’s) for commercial treatments and also use Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCT) for blood disorders.
Here’s a breakdown:
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells:
- These are the most common cells used in regenerative clinics today. MSCs are valued for their strong anti-inflammatory and healing effects. They are typically sourced from:
- Bone marrow: collected from the hip bone
- Adipose (fat) tissue: taken through a small liposuction-like procedure
- Umbilical cord tissue: donated after birth and expanded in a lab
- Bone marrow: collected from the hip bone
- These are the most common cells used in regenerative clinics today. MSCs are valued for their strong anti-inflammatory and healing effects. They are typically sourced from:
- Hematopoietic Stem Cells:
- These are the stem cells that form blood and immune cells.
- HSCT (Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant) has been a standard, life-saving treatment for decades in conditions like leukemia, lymphoma and multiple myeloma.
- In this procedure, patients receive high-dose chemotherapy or radiation, followed by an infusion of stem cells to rebuild the blood and immune system.
You may have heard of other cell types being used, but they’re mainly used in experimental trials. You can learn more about all the cell types out there in our Types of Stem Cell Article.
Looking into how Stem Cell Treatments actually work? Our team can walk you through how it works for your specific condition, costs & options across countries.
Get Free GuidanceNo pressure. No spam. Just honest advice to help choose the right clinic.
Can Mesenchymal Stem Cells Be Rejected in My Body?
Mesenchymal stem cells are rarely rejected by the body, with studies showing that allogeneic MSC therapies are usually well tolerated and do not require immunosuppressant drugs.
One of the biggest concerns patients have is whether their body might “reject” stem cells the way it can reject a transplanted organ.
With mesenchymal stem cells, the risk of rejection is very low. Clinical studies since 2018 have shown that allogeneic MSCs , meaning MSC cells not from your own body, are usually well tolerated without the need for immunosuppressant drugs.
Here’s what researchers have found:
- No classic rejection: Unlike organ transplants, patients receiving MSCs don’t experience the severe rejection syndromes doctors worry about with kidneys or hearts.
- Mild immune responses are possible: Some patients form temporary antibodies against donor MSCs, but this hasn’t been linked to dangerous side effects.
- Cells don’t last forever: Even if the immune system eventually clears the donor cells, they often remain long enough to release their beneficial healing signals.
Researchers are still keeping a close eye on this, especially for patients receiving multiple infusions or cells from different donors. But overall, the evidence is reassuring: MSC therapies are considered safe and are not associated with the type of catastrophic rejection seen in organ transplantation.
Why Are Immunosuppressants Sometimes Used?
MSC treatments rarely need immune suppression, but more complex replacement therapies sometimes do:
- MSCs (used in most clinics): Do not usually require immune suppression, since they are immune privileged.
- Cell replacement therapies (like lab-grown insulin-producing islet cells for diabetes): May require immunosuppressants to protect the new cells, because the immune system can see them as foreign.
- Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplants (HSCT) for blood cancers: Almost always require immunosuppressants, to prevent complications like graft-versus-host disease.
If they’re so safe, why don’t all Countries allow Umbilical Cord Derived MSCs Everywhere?
Even though studies show donor-derived mesenchymal stem cells are usually safe and rarely rejected, some countries like Japan & most in Europe have chosen not to allow them in clinics.
The reasons are mostly regulatory, not because of frequent rejection problems:
- Safety first: Regulators want more long-term data from large groups of patients before approving donor MSCs for widespread use.
- Mild immune responses still happen: While serious rejection is rare, donor MSCs can sometimes trigger antibodies and regulators want to be sure this doesn’t affect long-term safety or outcomes.
- Preference for autologous cells: Using your own cells removes the rejection risk entirely, so countries like Japan lean toward this as the lower-risk option.
- Strict standards: Allogeneic therapies require donor screening and consistent lab manufacturing. Some countries won’t approve them until those processes are tightly standardized and monitored.
How long do mesenchymal stem cells live after Stem Cell Therapy?
Most mesenchymal stem cells only survive in the body for a few days to weeks, but the healing effects can last much longer because of the signals they release.
- Short survival time: Studies in humans show that donor MSCs rarely engraft long-term. After an infusion or injection, most MSCs disappear within days or weeks.
- Lasting impact: Even after they are cleared by the immune system, MSCs leave behind anti-inflammatory and healing signals that can keep working for weeks or months.
- What this means for patients: You don’t need MSCs to “live forever” in your body for them to help. They act more like a temporary medicine factory than a permanent implant.
These findings were backed up by a review completed in 2025 & conducted by researchers in Iran.
Difference Between Cultured vs. Minimally Manipulated Stem Cell Treatments
Cultured stem cell treatments isolate and expand mesenchymal stem cells in a lab, while minimally manipulated treatments are same-day injections of mixed cells rather than true MSC therapy. Here’s a deeper explanation:
Minimally Manipulated Stem Cells
What it means: Cells are collected from your own body, processed the same day and given back to you. These samples contain a mix of cells but the stem cells are not isolated or multiplied.
- Quick, same-day procedure.
- Often seen as lower risk since the cells are used almost exactly as they were collected.
- The number of stem cells is limited.
- You’re not getting true Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy and the mix may be less potent compared to cultured therapies.
These are the treatments you’re getting in the UK & across Europe/parts of the US. If you’re getting treatment & the clinic is telling you the dosage in ML, not by cell count, you’re getting minimally manipulated treatment.
Cultured (Expanded) Stem Cells or Higher Dosage Treatments
What it means: Mesenchymal stem cells are first isolated and then grown in a lab until millions of cells are available.
- Higher doses of cells may allow stronger or longer-lasting effects, especially for conditions that need large amounts of regenerative support.
- Requires advanced lab facilities, higher cost and stricter regulatory oversight.
These are the treatments you’ll get across Japan, South Korea & in lesser regulated countries. When you see treatments offering 10 or 100 Million Stem cells, it means the cells have been “cultured” in a lab.
Stem Cell Therapy Treatment Process
Consultation and Evaluation
You start with a medical assessment to review your condition, medical history and whether they are a good candidate for stem cell therapy. You’ll need to provide medical records and imaging for clinics to be able to see if they can help or not.
If you get clinics giving you treatment plans without getting these details, this should raise some red flags.
Cell Collection
Autologous treatments:
- If they’re using MSC Cells from your bone marrow, they’ll get these cells from your hip bone.
- If they’re using MSC Cells from your fat tissue, they’ll use a small liposuction procedure to get these cells from your lower stomach area.
Allogeneic treatments (donor cells): Cells are sourced from screened and donated umbilical cords, placenta or bone marrow. These are processed in advance and will be ready by the time you arrive at the clinic.
Processing
Minimally manipulated therapies: The cells are concentrated the same day and prepared for reinjection without expansion.
Cultured therapies: The cells are isolated and grown in a lab for weeks before being given back to the patient. If you’re using your own cells, you’ll need to wait circa 6 weeks after they take the cells from you before getting treatment.
Administration
The prepared cells are delivered to the patient. Common methods include:
- Localized Injections into joints or tissues (e.g., knees, spine, skin).
- Intravenous (IV) infusion for systemic conditions such as autoimmune disease or COPD.
Recovery and Follow-up
The whole process is normally completed within one week. Recovery time depends on exactly the condition you’re getting treated. But it’s not invasive; you won’t be on crutches or need further support after treatment. You’ll be able to do day to day activities pretty much straight away.
During this process, you want to make sure the clinics are working with labs following best practise, have experience delivering the specific treatment you need & are actually using real Mesenchymal Stem Cells.
The biggest risk in Stem Cell Therapy is choosing a poor quality clinic. That’s why we take our process so seriously. We continuously vet every clinic on our platform to make sure you’re giving yourself the best chance of success & wont be getting any infections or contaminations.
What diseases can be treated by Stem Cells?
Most common conditions that are being treated with Stem Cells globally are orthopedic, cosmetic and anti aging.
Stem cell therapy is being studied and in some cases already used for a wide range of medical conditions. Research is ongoing, and results can vary depending on the disease and type of cells used. The most common conditions being treated globally are:
- Orthopedic Conditions: Osteoarthritis, cartilage injuries, tendon and ligament damage and chronic back pain
- Cosmetic & Regenerative Medicine: Applications include hair loss treatments, skin rejuvenation and anti-aging approaches.
Other Conditions that clinics are treating in some countries are:
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Exploring ways to improve heart function after heart attacks or in heart failure.
- Neurological Disorders: Clinical trials are testing therapies for Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury and stroke recovery.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn’s disease are being investigated for MSC therapies that reduce inflammation.
- Diabetes: Early research is looking at whether stem cells can replace or support insulin-producing cells, especially in type 1 diabetes.
To learn more about the conditions they can treat, we’ve got an article covering all the conditions here or check out our areas of treatment section.
Where can I get Stem Cell Therapy?
Most countries offer Stem Cell Therapy at some level, the most popular countries right now are the likes of Mexico, Colombia, Thailand, Japan & Ukraine.
Now legal regulations are different across all countries & in a lot of cases & it can get extremely confusing. Main differences include legality, types of cells used and if they’re allowed cultured treatments
To compare different countries, our article on Best Countries for Stem Cell Therapy might be an interesting read.
Best Stem Cell Therapy clinics Globally
We don’t let any clinic just sign up or pay to be listed.
We speak to every clinic directly and review their medical team, the treatments they offer, how their stem cells are sourced and how they follow up with patients after treatment.
We also review licensing documents to confirm they meet the legal and medical standards of the country they operate in. For example, whether cells are processed in a GMP-certified facility or if they provide documentation on stem cell quality.
Clinics must also agree to let us collect and publish independent patient reviews. Both positive and negative.

Why Use Alt Treatment?
We don’t just list clinics, we help you choose the right one, get the best pricing and support you through the entire journey. For free.
Compare with Confidence: Get clinic matches based on your condition, location, and budget.
Ask the Right Questions: Know what to ask before committing
Save on Treatment: Unlock exclusive discounts on vetted clinics and follow-up care.
We’re With You After Treatment: We check in post-treatment and help resolve any issues.
Travel & Visa Help: Need to travel for care? We can help with logistics, documents, and local tips.
Found a Clinic Elsewhere? We’ll check their licensing and track record for you, free of charge.
No Strings Attached: Even if you choose a clinic we don’t partner with, we’re still here to help you make the best decision.
Top Stem Cell Therapy Clinics Globally
We’ve vetted Stem Cell Therapy clinics Globally. Information on their processes, standards they follow & prices are on their profiles.
Compare ClinicsWhat are the negative effects of Stem Cell Therapy?
Negative effects of Stem Cell Therapy include infections from choosing poor clinics, pain at injection sites & spending a lot of money on a treatment that might not work.
To learn more about the side effects, check out our article on Stem Cell Therapy Side Effects.
Stem Cell Treatment Cost in 2025
Stem cell treatment costs range between $1,320 and $50,000 globally according to actual data we’ve collated from Stem Cell Clinics and patients directly.
Factors depend on:
- What country you’re visiting
- Condition you’re getting treated
- Cell Volume.
Most clinics in each country will operate to similar levels as each other. One thing we’ve found is surprisingly, treatment in the West in countries like the UK or US aren’t necessarily more expensive.
The treatments are less advanced but they’re not extremely more expensive than countries like Colombia, Panama & Japan.
To break down treatment costs by country, check out our guide on Average Costs Globally.
Not sure which country’s right for you?
Browse verified stem cell clinics in Colombia, UK, Thailand and more that we’ve already personally vetted.
Browse Verified Stem Cell ClinicsShould I get Stem Cell Therapy in 2025
Totally depends on your current condition, financial situation & risk tolerance.
From a research perspective, it is still early but there’s been some interesting results and a lot of countries are advancing their laws around Stem Cell Treatments.
The likes of Japan, South Korea, Indonesia, Costa Rica, Dubai have all legalized Stem Cell Therapy in different forms. The US has made some recent changes as well, with Utah & Florida both offering umbilical cord derived Stem Cell treatments.
It can help, but be aware nothing is guaranteed at this stage.
If you are set on getting stem cell treatment, the biggest risk will come from choosing a poor quality clinic. So make sure you’re doing your due diligence or reach out to us if you need support on your journey.
If you’re deciding which country is best for you, or want to talk about clinics we’ve already vetted, fill out our form below. Our team will guide you with clear, honest answers.
Alt Treatment is a free, independent platform that helps you understand stem cell therapy & decide if it’s right for you.
We break down complex information into clear, honest guidance. When you’re ready, we can connect you with verified clinics that meet your needs, in the right location & often with exclusive discounts.
There’s no charge to use our platform. No hidden fees. No pressure. Our main aim is to genuinely help you figure out if treatment is right & the best places to consider.
If you want to talk, fill out our form here & our personal concierge team will reach out.
Stem cell therapy is used to reduce inflammation and support healing in conditions like arthritis, back pain, autoimmune diseases, neurological disorders, diabetes and some cosmetic treatments.
Cheapest places for Stem Cell Therapy are Mexico, Ukraine, Thailand & India. There’s differences in each region, check out our article on the Best Countries for Stem Cell Treatments
Recovery varies based on the condition and type of therapy. It can range from days to weeks.
Mesenchymal stem cells. Their versatility makes them one of the most widely used types.
Right now, stem cells haven’t been proven as a cure for Alzheimers, but early data has shown it can help slow down the progression of the disease & symptoms. To read more about how Stem Cells can help with Alzheimer’s, our article on Stem Cell Therapy for Alzheimer’s might be useful.
Or, if you want to see how stem cells can help other conditions, check out our Areas of Treatment Section.
Fill in your details below
For a discounted offer for Stem Cell Therapy!