Stem Cell Therapy for Alzheimer’s has made huge strides in the last 5 years or so.
Alzheimer’s is a progressive brain disease that slowly erodes memory, thinking, and independence. It’s the most common cause of dementia and despite decades of research, there’s still no cure. The drugs we have today offer only modest benefits, often focused on slowing symptoms, not reversing them.
That’s where stem cell therapy for Alzheimer’s comes in. Scientists are exploring whether certain types of stem cells can reduce inflammation, protect brain cells & maybe even regenerate parts of the brain damaged by the disease.
In this article, we’ll break down how stem cells treat Alzheimer’s, the latest research and where treatment might be available today.
What Is Alzheimer’s Disease, Really?
Alzheimer’s is more than just memory loss. It’s a progressive brain disease that damages and destroys brain cells over time, leading to confusion, personality changes, and eventually the loss of basic functions like speaking and walking.
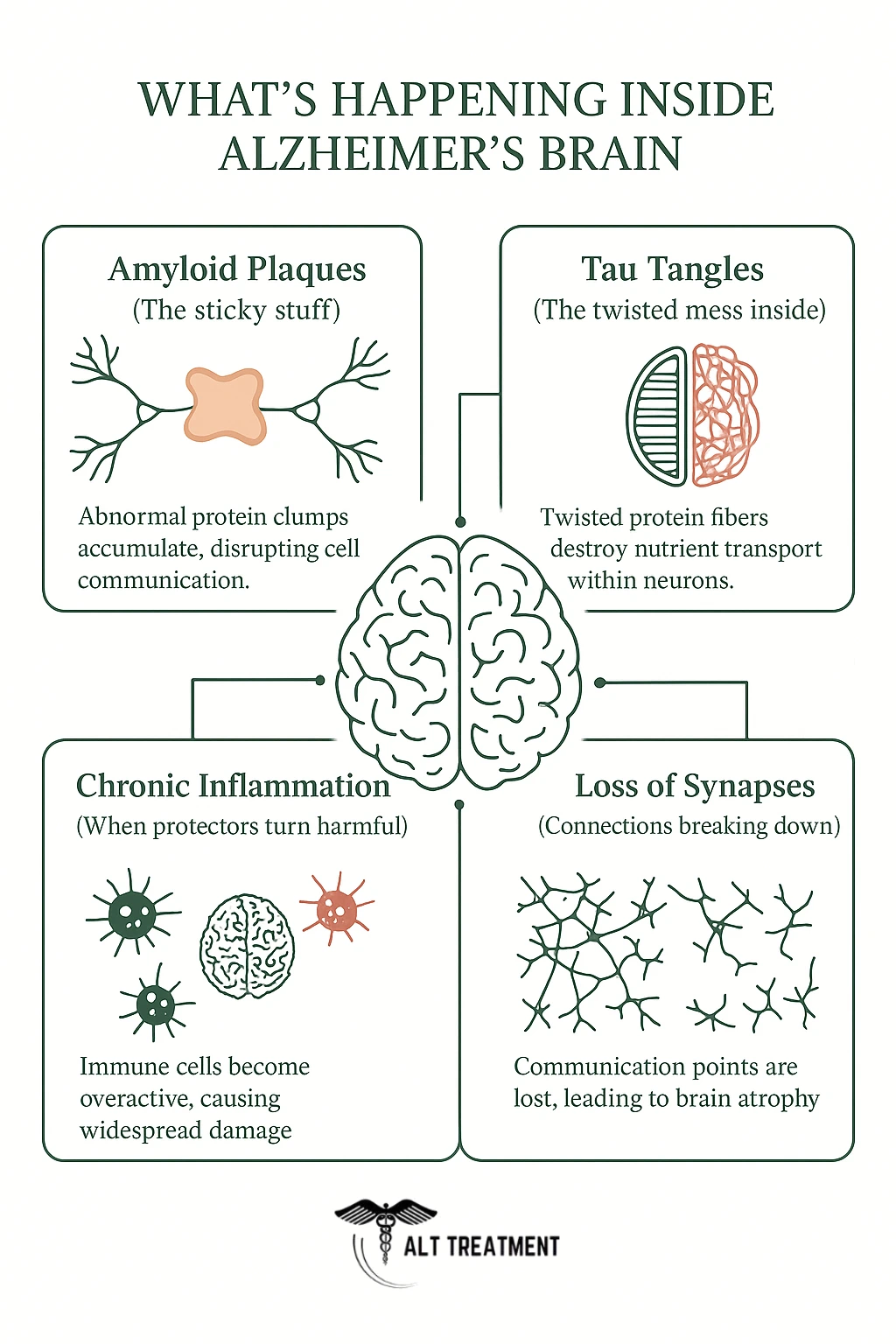
But what’s really going on inside the brain? Scientist’s have identified these factors so far:
- Amyloid Plaques (the sticky stuff)
Tiny bits of protein called amyloid-beta clump together between brain cells and form sticky plaques. These interrupt communication between neurons and may trigger inflammation and cell death. - Tau Tangles (the twisted mess inside brain cells)
Inside neurons, another protein called tau becomes faulty and forms twisted fibers known as neurofibrillary tangles. These block the transport system within brain cells, causing them to break down and die. - Chronic Inflammation
The brain’s immune cells, called microglia, are supposed to clean up waste and protect neurons. But in Alzheimer’s, they become overactive, leading to chronic inflammation that actually damages healthy brain cells instead of helping them. - Loss of Synapses and Brain Shrinkage
As more neurons die, the brain literally shrinks. Connections between brain cells (called synapses) disappear, especially in areas related to memory, thinking, and behavior.
Why doesn’t normal medication work for Alzheimer’s?
Traditional drugs aim to boost memory or slow symptoms but they don’t fix the damage or stop the root causes. That’s why scientists are turning to stem cell therapy: to reduce inflammation, protect remaining neurons & possibly even repair or replace lost brain cells.
What Is Stem Cell Therapy for Alzheimer’s?
Stem cell therapy for Alzheimer’s is an experimental treatment being studied for its potential to slow memory loss, reduce brain inflammation and protect or repair damaged brain cells.
You can read more on how it works here & here. Or we’ve broken it down for you below
Alzheimer’s can be frustrating and overwhelming to treat. We’re not here to hype miracle cures. Our goal is to help you decide for yourself if it’s worth exploring, risks involved & treatment price ranges in different countries.
Get Free GuidanceNo pressure. No spam. Just honest advice to help choose the right clinic.
Types of Cells used for Alzheimer’s Stem Cell Treatments
There are a few types of stem cells being used so far:
- Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs): typically from fat tissue, bone marrow, or umbilical cord. These are the main ones being used in actual treatments from clinics.
- Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs): reprogrammed from a person’s skin or blood cells
Alzheimer’s Stem Cell Therapy Cost 2026
As of 2025, costs of Alzheimer’s Stem Cell Therapy costs can go up to $35,000. Costs will vary depending on volume of cells & delivery methods. Typically, any clinics offering Intrathecal injections will charge more.
We’ve gathered our pricing data in a few different ways & we’re always updating it!
How Stem Cell Therapy treats Alzheimer’s specifically
Here’s how scientists think Stem Cells can help treat Alzheimer’s:
Reduce Brain Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a major driver of Alzheimer’s. Stem cells, especially MSCs can release anti-inflammatory signals that help calm the brain’s immune response. This creates a healthier environment that may slow damage and protect brain tissue.
Support Existing Brain Cells
Rather than replacing neurons, some stem cells release neuroprotective factors that help current brain cells survive longer. Think of it as boosting the brain’s ability to protect itself from further decline.
Encourage New Neuron Growth
Certain stem cells may help form new brain cells, especially in memory-related regions like the hippocampus. While it’s still early, this could one day help replace neurons lost to the disease.
Restore Immune Function
A major breakthrough from Stanford showed that replacing damaged immune cells (in mice) in the brain (called microglia) with healthy ones restored their ability to clean up toxic proteins like amyloid-beta.
Personalized Repair Using iPSCs
Researchers are exploring whether iPSCs can be used to create healthy brain cells in the lab, and then transplant them into the brain to replace cells that have been lost or damaged by Alzheimer’s. These new cells might help by:
– Supporting connections in parts of the brain responsible for memory and thinking
– Supporting nearby brain cells by releasing helpful growth factors
– Reducing inflammation and slowing further damage
How Is Stem Cell Treatment Delivered for patients with Alzheimer’s?
For commercial treatments, Stem Cells are delivered through an IV are the most common right now. Some clinics will also offer Intrathecal injections too.
Intravenous (IV) infusion
Stem cells are dripped into a vein through an IV, usually in the arm. This is the most common method used by private clinics because it’s simple, low-risk, and doesn’t require surgery.
- Limitations: It’s unclear how many stem cells actually cross the blood-brain barrier using this method.
Intrathecal injection
Stem cells are injected directly into the spinal canal. Some early-phase studies are testing this approach because it brings the cells closer to the brain.
- Limitations: It has more direct access to the brain but carries greater risk of infection or nerve injury.
Intracerebroventricular (ICV)
Cells are injected directly into the brain’s ventricles through a device (usually an Ommaya reservoir) implanted under the scalp. This allows direct delivery to the brain, bypassing the blood-brain barrier.
- Limitations: This is only used in highly controlled hospital-based trials. It’s way too invasive for commercial use.
Intranasal (Nasal Spray)
Stem cells or their exosomes are sprayed into the nose, aiming to reach the brain through the olfactory nerves. It’s mainly used in trials and rarely used in clinics.
- Limitations: This is a newer approach with promising early results, but it is still highly experimental.
This table summarises the delivery methods
| Delivery Method | Invasiveness | Direct Brain Access |
| IV Infusion | Easiest | Indirect |
| Intrathecal (Spine) | Moderate | Moderate |
Intraventricular (Brain) | High | Direct |
| Intranasal (Spray) | Easiest | Indirect |
Looking into Stem Cell clinics for Alzheimer’s?
Browse verified stem cell clinics in Colombia, Japan and more that we’ve already personally vetted.
Browse Verified Stem Cell ClinicsCan Stem Cell Therapy Cure Alzheimer’s Disease?
Research is showing whilst Stem Cell Therapy isn’t a cure for Alzheimer’s, it can potentially slow the progression of Alzheimer’s.
The goal of research currently isn’t to reverse or cure Alzheimer’s but to see if Stem Cell Therapy can safely manage the disease.
What does the Research say about Stem Cells treating Alzheimer’s?
Research into stem cell therapy for Alzheimer’s is still early, but the signs are promising. Across over a dozen clinical trials, patients have seen improvements in memory scores, reduced brain shrinkage, and lower levels of harmful proteins like p-Tau and amyloid. Some even showed changes in brain metabolism and inflammation.
Most studies are still small (usually under 50 participants), and many don’t include control groups. So while the results are encouraging, they aren’t strong enough (yet) to confirm stem cells as a proven treatment. Larger, longer-term trials are still needed.
The research is happening globally, with major studies led in:
- The United States
- China
- South Korea
- And Japan, which pioneered iPSC-based therapies
We’ve compiled all the research and broken it down for you here.
How successful is stem cell therapy for Alzheimer’s?
Early clinical trials show stem cell therapy for Alzheimer’s can improve memory scores in up to 60–80% of patients, but results vary and remain unproven.
RB-ADSC Trial (U.S.):
In this small Phase 1 study, 80% of patients showed a drop in p-Tau, one of the toxic proteins tied to Alzheimer’s.
Even better? 60% improved on memory tests (MMSE), and there were no serious side effects reported up to 23 weeks after treatment.
Lomecel-B Trial:
This study focused on brain shrinkage and the results stood out. Patients who got stem cells had 48% more brain volume preserved and slowed hippocampal loss by nearly 62%. That’s a big deal, considering how fast the brain typically deteriorates in Alzheimer’s.
But remember, these studies were tiny & super early stage.
Top Stem Cell Therapy Clinics for Alzheimer’s

Is Stem Cell Therapy for Alzheimer’s Safe?
Early trials suggest stem cell therapy for Alzheimer’s is generally safe, with no serious side effects reported in most studies & reviews.
In fact, safety has been a consistent finding across different delivery methods. Including IV infusion, nasal sprays and even direct brain injections.
That said, most trials are still small, and long-term safety beyond 6–12 months hasn’t been fully studied. Larger studies are needed before stem cell therapy can be declared fully risk-free. But so far, it looks promising.
Promising Alzheimer’s Treatments in 2026
While stem cells are one of the most exciting areas of research, scientists are exploring several other cutting-edge treatments. These aim to slow or stop the disease, not just mask the symptoms.
| Treatment Type | What it Does | Stage |
Anti-Amyloid Antibody Drugs | Clears amyloid plaques from the brain | FDA-approved (e.g. Leqembi), ongoing trials |
| Anti-Tau Therapies | Targets and neutralizes tau protein tangles | Early to mid-stage clinical trials |
| Gene Therapy & CRISPR | Edits or silences genes linked to Alzheimer’s | Preclinical and early-stage trials |
| Alzheimer’s Vaccines | Trains immune system to attack amyloid or tau | Phase 1 and 2 trials underway |
| Neuroinflammation Blockers | Calms inflammation in the brain’s immune cells | Early trials, some drugs repurposed |
| Metabolic & Hormonal Therapies | Targets metabolic or hormonal dysfunction linked to Alzheimer’s | Mixed, some in trials, others experimental |
Is it Worth getting Stem Cells for Alzheimer’s?
If you have no other options, potentially. Stem cell therapy for Alzheimer’s is no longer just a futuristic idea, it’s something scientists and clinics around the world are actively testing. From intravenous infusions to nasal sprays and direct brain injections, researchers are exploring how different types of stem cells might reduce inflammation, protect brain cells, and slow down memory loss.
Early results are promising. Some studies show improvements in cognition, others show slower brain shrinkage, and nearly all have shown that stem cell therapies are safe, at least in the short term. But we’re still in the early phases. Most trials are small, and we don’t yet know how long the benefits last or which patients respond best.
Clinics in places like Japan, Colombia, and India are already offering these treatments, often outside of formal trials. Nothing has been definitely proven yet, but some clinics have had some amazing success stories come out. If you’re thinking about getting Stem Cells for your Alzheimer’s, understand there’s no guarantees it will work right now.
Alt Treatment is a free, independent platform that helps you understand stem cell therapy & decide if it’s right for you.
We break down complex information into clear, honest guidance. When you’re ready, we can connect you with verified clinics that meet your needs, in the right location, and often with exclusive discounts.
There’s no charge to use our platform. No hidden fees. No pressure. Our main aim is to genuinely help you figure out if treatment is right & the best places to consider.
If you want to talk, fill out our form here & our personal concierge team will reach out.
Stem cell therapy for Alzheimer’s is still experimental, but yes, some clinics are already offering it. Early studies show it may reduce inflammation and slow memory loss but it’s not a proven or approved treatment yet.
Right now, most treatments range from $10,000 to $25,000. It depends on where you go and what kind of stem cells are used. These are rough estimates, we’re working on getting exact prices by country, so bear with us!
No, the FDA hasn’t approved Stem Cell Therapy for Alzheimer’s.
Right now, the most promising treatments include anti-amyloid drugs like Leqembi (FDA-approved) and experimental therapies like stem cells, which aim to slow memory loss and reduce brain damage. Both are being actively studied in clinical trials.
Japan, Colombia, South Korea, & Panama are amongst the countries you can get Stem Cell Alzheimer’s treatments in. To view clinics globally that can treat Alzheimer’s, you can compare them all here.
Fill in your details below
For a discounted offer for Stem Cell Therapy!
